Surviving apparel manufacturing business in the current situation in India is tough. Industry is running on ‘maturity stage’ of the ‘life cycle of business’. For surviving, the only option is to reduce cost with lesser lead time and higher quality of goods produced. The ‘integrated and continuous production line’ in apparel manufacturing fulfils all these three aspects. This line system is also known as online system and carries out many aspects of lean production system.
‘Continuous production line’ is different from traditional production methodology where right from raw material till packing, many different departments like storage, cutting, sewing, finishing and packing function as separate entities. Therefore, keeping coordination between departments, the extra movement and multiple quality inspections along with multiple audits in-between the departments need extra manpower which can be eliminated. One production line of 40 to 50 pieces of hourly output (formals and fashionwear) has been taken as sample line to explain the new line system.
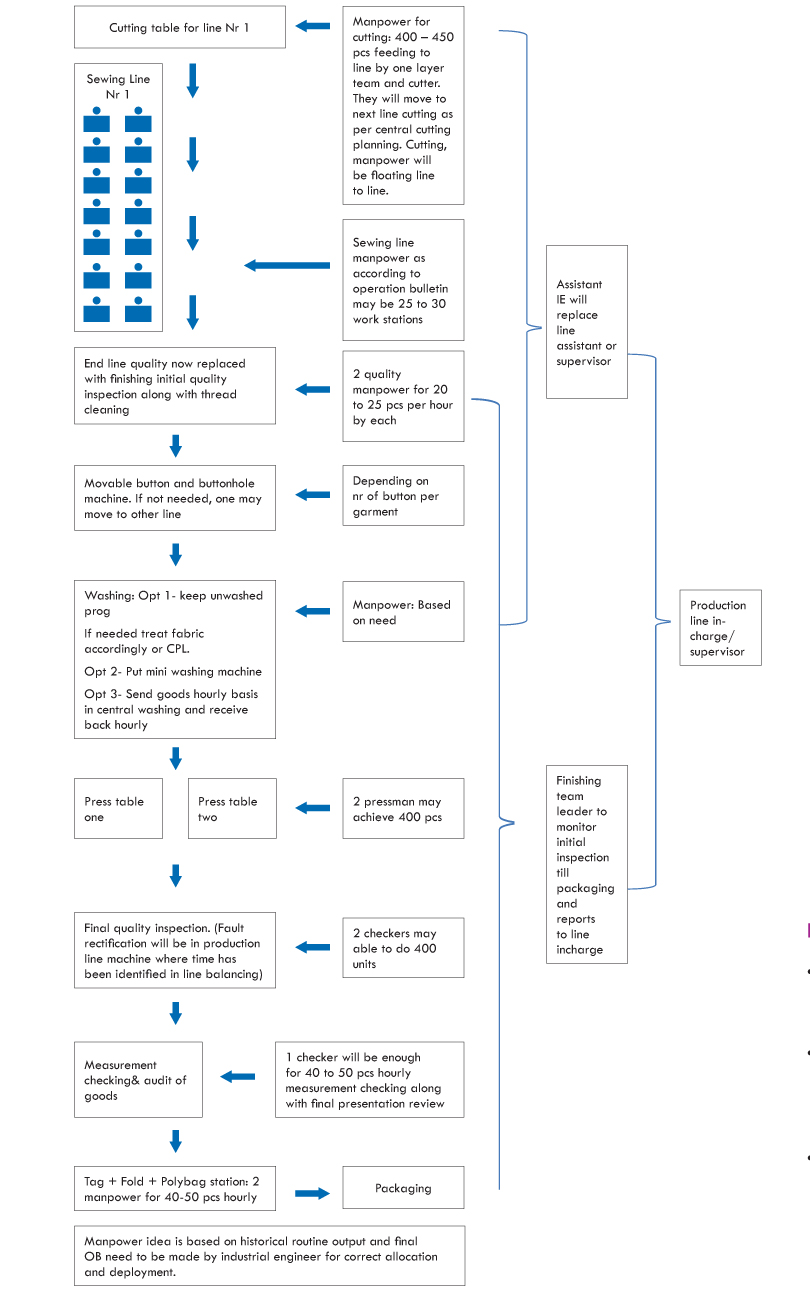
Integration of various production departments is continuous production line. Even one can integrate right from storage till packed goods for every production line. This may depend on space and layout of factory. In a study here, cutting till the packing process integration has been explained.
Integrated and Continuous line structure diagram
(This may be only an idea and may get change based on space and layout of factory, but the flow must be continuous and integrated)
Department-wise points to be taken care of:
Pre-production:
- Planning must be ready with all raw materials available. Normally wash care label due to testing parameters and packaging trims like tag, price ticket, polybag, etc. get delayed.
- Merchandising team must have all approvals right from raw materials till packaging.
Cutting:
- Line-wise table allocation and cutting as per daily line feed needed.
- Cutting manpower will work as floater. Suppose line is balanced on 400 pieces, then layer man and cutter will cut those many cutting only and move to next line cutting. Certainly they will follow the cut plan while moving and cutting line-wise.
- Based on space and factory layout, some of the cutting operations like fusing, numbering and bundling may club 2-3 lines together but near to sewing lines only
- Benefits:
- Production line will always be aware about the cutting available stock. One standard apparel factory line in India loses about 3-8 per cent of line efficiency due to cutting not available on time. This happens due to feeding delay because of centralised cutting (geographical distance, coordination issue, etc.) which is now sorted out due to continuous production line.
- 1 to 4 per cent efficiency of line goes down due to quality issue in cutting. If production line has the cutting near to line and has access, then cutting defect per cent will go down. However, in general scenario, the cutting process happens away from sewing line and when cutting quality issue appears in production line, there are delays in communication and sometime smaller defects are ignored by line supervisor.
- Better utilisation of manpower – If cutting has any crisis and sewing line has unbalanced manpower or free manpower during style changeover of line, the manpower may get used in cutting.
Industrial Engineering:
- While production line balancing, the balancing should be done till packing.
- While line balancing, the one less occupied machine operation need to be allocated for finishing alteration.
- One line need to have one supervisor/in-charge and should be assisted by one Junior IE and one finishing and packing team leader. One junior IE each line instead of line assistant will be fruitful.
- Along with routine IE work of motion and time study, synchronisation, layout , work study, line balancing, etc., line employees need to be explained and trained for skill upgradation and new requirement
Sewing:
- While stitching in line, there should be no mishandling and stain creation.
- Instant quality control and if any quality deviations need to be freeze as soon as possible.
- No holding of alterations and immediate rectification is needed.
- Instant approvals for any hold or deviations. Any decision or approval should not be kept pending.
- Online thread trimming:
- One standard men’s shirt will have external uncut thread only on collar finish, pockets, cuff finish, sleeve plackets, bottom and labels. Rest all the threads will either auto cut by another operation or get hide inside. Therefore, if we put UBT on this 7-8 operations or train our operators to cut threads from root, they will able to achieve thread trimming issue.
- Similarly for any style identification of operation where external thread may appear, one may put UBT and train operator to trim from edge. For example, to control uncut sewing thread in one standard men’s shirt – collar finish, main label if not inserted in collar, pocket attachment, sleeve placket, cuff finish, wash-care if not inserted in side hem and bottom hem need to be placed with UBT. While making OB of any garment, the IE department specifies the operation where UBT is specifically needed. Normally, UBT is put on smaller and clean operations like main label attachment etc. or wherever needed as defined by R&D department. In new thought, OB maker will start thinking on operation where external thread would appear like the men’s shirt example given above. It is applicable where scarcity of UBT machines is there.
- In our training, this also would be an important area to explain about sewing thread trim from edge itself to all the operators because at the stitching starting point, even UBT machine leaves uncut thread.
- The continuous line would eliminate multiple counting and multiple transports of garments. In a traditional factory, this happens when it completes one process and shifts to next process between departments. For example, after cutting, counting is done and then audits before shifting to sewing, after stitching, do the audits, then count and transport to finishing storage.
Quality:
- The end line quality check of sewing will be replaced with finishing initial/primary checking. For one standard sewing line of 40-50 pieces per hour output line, two checkers will be enough. These two checkers will inspect thoroughly 20-25 pieces in an hour with all quality parameters along with thread trim. Thread trimming also would be considered as defect and they would control the trimming in line itself as explained above on how to do online thread trimming, with the help of line in-charge and line roaming quality inspector.After the complete product formation, end line is first and through checking station and also it is considered as finishing primary checking therefore timing given is more on this point. Also these two checkers will have to control sewing thread trim as added work for them. However in-house production line made garment measurement checking a faster work because only wrong sizing needs to be controlled. Therefore, only 2-3 measurement points where size-wise deviation seems more normally are measured. Checker, while doing repetitive work, remembers the measurement. The normal hourly capacity of finishing measurement checking is 80 to 100 garments per hour.
- Quality defects need to be controlled instantly and on originating machine itself by using quality control tools like Pareto chart, 80:20 rule, root cause analysis, preventive and corrective action, etc. Any alterations need to be rectified immediately.
- Since the buttoning and ironing is instantly happening, any defect or feedback from final inspection of goods must get communicated to the originating operation on instant basis to control immediately.
- Elimination of multiple inspections and audit after every process.
The points which will fail this system:
- If all technical and styling approvals not available from the merchant and goods get hold in line.
- If complete trims not available especially the wash care label and packagingmaterials like price ticket, tags and polybag, etc.
- If any operation hold in line, delay in decision, machinery breakdown for longer time, apparatus not available etc.
- Defective goods hold and instantly not rectified.
- If employees not been properly explained, trained and correct skill not deployed on correct position.
Total projected benefit:
From one 40 to 50 pieces average per hour balanced sewing production line following will be saved:
– .25 manpower for cutting transport.
– 5 per cent efficiency loss due to cutting no feeding and 2 per cent efficiency loss due to quality fault in cutting.
– Sewing quality up due to cutting quality improvement.
– 2 manpower of stitching end line checkingelimination and replaced with finishing initial check.
– .5 manpower for count and pcs transport from stitching to finishing storage
– .5 manpower of sewing audit before sending goods to finishing storage
– 2 manpower of finishing thread trimming
– Finishing quality up due to no storage after stitching of goods and instant fault feedback to sewing line because of instant finishing.
= Total 5.25 manpower from 400 to 500 pcs of one production line along with hidden and unaccounted benefit of cutting, sewing and finishing quality and efficiency improvement. Monetary calculation may be done by particular wage rate of factory.
How it helps to cut cost:
- By eliminating extra manpower
- Improving efficiency by full engagement of manpower allocated
- Reducing line idleness by instant cutting feed
- Reduction in repair percentage in finishing due to online finishing and based on feedback production line take preventive action immediately.
- Reduction in WIP volume hence working capital
How it helps to improve lead time reduction:
- In traditional production system after stitching of garments, it goes to finishing storage. Finishing starts after many days, therefore in new way of production line where goods are getting finished instantly, it saves minimum 4-5 working days.
How it helps to improve quality:
- In traditional production system after stitching, ready goods go to finishing. The goods keep on waiting for finishing for days. By the time factory decides to finish, the stitching output is almost over or completely over. Then in finishing, we realise that measurements are deviating, workmanship is not as according to the need of buyer, etc. In new way of working, everything is happening continuously, therefore backward feedback instantly improves quality.
- In new line system, the end line check point is getting controlled by the finishing initial checking, the quality demand will increase, hence the product quality.
How it represents lean and six sigma:
- Elimination of multiple counts, audits and transport along with flow correction is all about lean.
- New line system improves processes with reduction in quality defects, reduction in cost, reduction in lead time etc. is all about six sigma.
Epilogue:
Proper plan, layout and engineering, style selection, manpower training, approvals and trims, etc. are the keys to success. Initially, careful approach is needed. Considering continual improvement, one may start converting one by one line. There may be different structure and line layout with different per hour output quantity, but one thing is sure that if the process gets integrated, the sure and certain gain will happen.